What is CRR?
CRR means: Cash Reserve Ratio
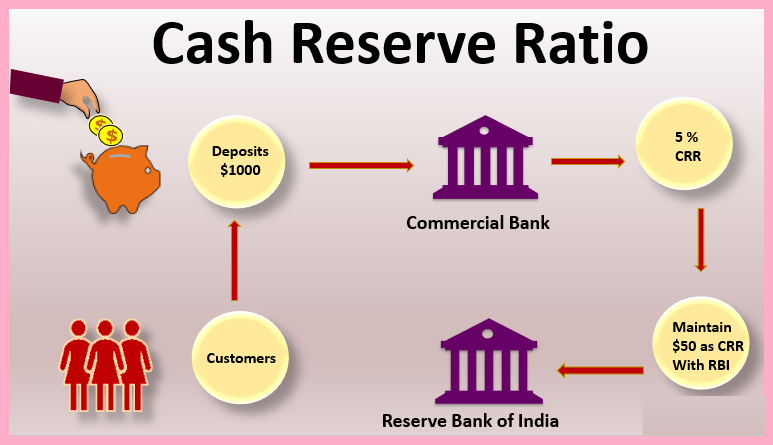
This ratio is an important tool determined by RBI, which helps in controlling the money supply and liquidity in the country. CRR determines the minimum percentage according to which all banks are required to keep some cash and deposits with the RBI as reserves. This percentage is fixed by RBI and every bank is required to follow it.
CRR works to reduce liquidity risk in the country’s economy, where if people need money at once during an emergency, then the bank has sufficient funds to meet the demand. All banks must deposit funds with RBI as per the CRR ratio, failing which they may have to face penalties.
How does CRR work?
CRR plays an important role in controlling financial stability and inflation in the country. This is an important part of monetary policy, which helps in controlling the flow of money in the country. Under this, banks have to keep a certain part of their deposits with RBI as reserve. By increasing or decreasing the CRR rate, the Central Bank maintains the financial stability of the country.
If the CRR rate in the country is high, then the bank has to keep a large part of its deposits with RBI. Due to this, less money is left with the bank and due to shortage of money, banks are not able to give more loans to people and businesses. Due to people not having much money, their expenses will reduce, due to which the demand for products and services will also reduce. If demand is low and supply is high, the price of products and services will be low, which helps in keeping inflation low.
On the contrary, if the CRR ratio is low then the bank will have more deposit money, which it will be able to give to people through loans and other lending tools. As people have more money, their spending power and demand will increase, which boosts the country’s economy and production.
How is CRR calculated?
There is no fixed formula to calculate CRR. Generally it is calculated as a percentage of Net demand and Time liabilities (NDTL) of banks. NDTL includes funding of bank’s savings account, current account, RD and fixed deposits etc.
For example, if the bank has Net Demand and Time Liabilities of Rs 500 crore, and the CRR rate is 4%, then the bank will have to keep Rs 2 crore with RBI as cash reserve ratio.
Importance of CRR
CRR is an important part of monetary policy and it helps in managing money in the country and controlling its flow in the economy. Apart from this CRR main features:
Financial Strength: CRR ensures that the bank has adequate funds available in the form of deposits at all times. In this way, in case of emergency, people do not have to face any kind of problem regarding money.
Control on inflation: RBI controls inflation by controlling the rate of CRR. As already mentioned, if the CRR rate is increased, it helps in controlling inflation, whereas by reducing CRR, demand and production in the economy is promoted.
Balancing liquidity: The flow of money in the country is controlled through CRR. This confirms that there should not be more money in the economy than is needed when needed and if the functioning of the economy is to be accelerated then funds and resources should be available to the people without any problem.
Base Rate: CRR plays an important role in deciding the base rate. Base rate is the minimum rate, considering which any bank can lend money to people as a benchmark.
Why is CRR changed?
According to economic and government policies, CRR is changed from time to time, and it is necessary to do so. When the economy or people have too much money, it causes inflation, because in case of more money, people spend more, which increases demand and due to increase in demand, inflation also increases. Through CRR, RBI can increase or decrease money and its flow in the country, which helps in controlling inflation. There are many such economic and financial reasons due to which the government has to make changes in CRR.
Current CRR rate
The current CRR rate in India is 4.5%. That means if a bank has a deposit of Rs 1000, then it will have to keep Rs 450 with the Central Bank as CRR.
Difference between CRR and SLR – Difference between CRR and SLR
| CRR | SLR |
| CRR means the ratio that the banks of the country have to maintain with the RBI. | SLR is the percentage of the bank’s deposits that has to be kept in the form of liquid assets such as gold, cash or government securities. |
| With the help of CRR, RBI manages the money supply and inflation in the country. | With the help of SLR, the Central Bank confirms that the bank has sufficient funds available and its condition is stable. |
| RBI has direct control over CRR ratio. | RBI has indirect control over SLR. |
| No interest is paid on the money kept with the Central Bank in the form of CRR. | Some interest may be given by the Central Bank on SLR funds. |
| If the bank does not follow the CRR ratio, it may have to pay a penalty. | The bank has to pay penalty for not maintaining SLR. |
Conclusion
CRR is an important tool of monetary policy which the Central Bank keeps using from time to time. It is used not only in India but by all the banks of the world, which works to maintain balance in the economic and financial condition of the country.

Gaurav Heera is a leading stock market educator, offering the best stock market courses in Delhi. With expertise in trading, options, and technical analysis, he provides practical, hands-on training to help students master the markets. His real-world strategies and sessions make him the top choice for aspiring traders and investors.